Intro: Duration: (01:54)
Opening music jingle & sound effects
Jeff Hunt:
Hi everyone, I'm Jeff Hunt, your host of the Human Capital Podcast. This is the place where we endeavor in each episode to uncover the deeply human aspect of work. Have you ever taken a personality assessment either at home or work? My guess is that you probably have and if you have, I'm curious about what your thoughts were about your assessment.
Was this a positive or negative experience? Has it helped you in your relationships at work or at home? Today we're gonna talk about the advantages and disadvantages of these assessment tools and take the time to do a deep exploration of one tool that I think provides significant value. In fact, we're gonna take two episodes to break this all down for you.
And I don't think you'll be disappointed. Let's talk about the assessment or testing industry for a minute. According to psychology today, approximately 80% of the fortune 500 companies in the US use personality tests to assess employees and potential candidates. This enormous industry exceeds 3 billion dollars a year.
But it's also a crowded market with a lot of variabilities. Some of the more common tests you might be familiar with include Myers-Briggs, caliper, disc, and strengths finders, and some advantages of these tools include things like improved self-awareness. And from a recruiting standpoint, the ability to understand candidates better.
The opportunity to shorten the recruitment cycle, and eliminate bias. And even in some cases, spot dark personality traits. And most organizations, have the goal of helping employees learn how to work better together. But however, there are some disadvantages, including the fact that many of these tools are inaccurate.
They can actually increase recruitment bias and there can be interpretation problems if you don't use a consultant. People can also make false assumptions about others based on their assessment type. And they can put people in categories or boxes. And the fact is that humans are much more nuanced than this.
And so, as I mentioned, we're gonna focus on one assessment today, which is called the Enneagram. And I personally have found tremendous value from this assessment. And I happen to know my guest believes this also. I actually don't know of a more qualified person to help me explore the Enneagram than Ginger Lapid-Bogda.
Ginger runs a consulting firm called The Enneagram in Business and is a consultant, and trainer, she's a coach and she has over 35 years of OD experience. Ginger has worked with fortune 500 companies, nonprofits, and service organizations, and has literally written the book on the engram in business. No, actually she's written four books.
With her fifth book coming out shortly. Ginger has trained over 500 professionals worldwide on how to use the Enneagram in their professional work. And she has her bachelor's degree from UC Berkeley, a master's from UPenn, and her Ph.D. from UC Santa Barbara. Welcome, ginger!
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Thank you very much, Jeff.
Jeff Hunt:
It is a great honor to welcome you to the show today, and I'm very excited to unpack the Enneagram with you over these two episodes.
And as I mentioned in today's episode, we're gonna focus on the background of the engram as an assessment tool. And then next episode, I am super excited to unpack your new book team transformations, right?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Well, the new title is: "Transform your team with the Enneagram, build trust, decrease stress, and increase productivity."
Topic 1. Who inspired you the most in your career? (04:05)
Jeff Hunt:
Fantastic. So I had the opportunity. Ginger gave me an advanced reading of this book before it comes out and I am highly recommending it, we have a lot to jump into today. I would love it, Ginger, if you could actually just start us out by giving us a thumbnail of your career journey, and take us back.
Through that journey and share also who inspired you the most along the way?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So, the short version of the long story, because I'm old enough to have a long story is I started out as a teacher and realized the importance of both learning cognitively and learning emotionally or interpersonally in being an effective learner and an effective teacher.
And so, I parlayed that I've worked in organizations for decades as a trainer, as a consultant, an OD consultant, as a coach, and about 25 years ago. I actually now have about 45 years on me in consulting. It's like really seriously long, but, about 25 years ago, I pat crossed paths with the Enneagram.
I didn't create it. It's actually 3,000 to 4,000 years old. We're not sure how old it is, but it's been evolving over centuries and it has had a modern rebirth. My sort of mission or passion is to bring it out into the organizational world so that organizations can be more effective. People can be more productive and happier at work and more satisfied.
And in the process, the second is that they really get to know themselves and others better. I think at this point, I probably, stopped counting, but maybe 2, 3000 professionals worldwide. I've trained. I don't know. I work directly with organizations and I write these books to help kind of foster that.
So I wanna say something that you said, and I think it's really important. It's the downside and upside. So the Enneagram or really, any assessment really should not be used for hiring, but the Enneagram types themselves, and there are nine of them, will tell you a lot about a person's patterns of thinking, feeling behaving.
Do you know that Jeff? And it will tell you a lot about their worldview. And so there is a great value to these nine perspectives, but hiring should be based on skills for the job, and experience, although, experience is a tricky thing because you know, you take a person who's had 20 years of experience, but they've been doing that the same thing over and over.
And somebody who's had eight years of experience, but they learn from it. So I say, which person would you hire? The other is that what really is relevant to hiring because it makes a more effective employee besides skills and experience is their level of self-mastery. Their ability to, as you know, understand themselves, work with themselves, not be reactive, but be more conscious, and choiceful.
And the ability to work with all kinds of other people effectively. Now the underground helps people develop self-mastery, but type itself, you can get a low self-mastery person of any type and they can destroy a team or they're at the top. Takes about three months to destroy a thought.
If you have a thought leader who's highly dysfunctional, no matter what their type. And I'd say three years to rebuild it after finally, they leave.
Topic 2. Why is personality assessment used in the workplace? (07:32)
Jeff Hunt:
Wow. I want to go a little deeper into the assessment space. Can you render your opinion about why so many personality assessments are actually used in the workplace today?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
There is a big market financially and a lot of financial gain for people who provide that. So, there are lots of offers from the point of view of employers. How do we know how to hire well? Because the cost of a bad hire is huge and it's getting more so, and the higher the level you're hiring for the more significant the role.
The worst a bad hire is. So, people are like, how do I know how to hire people? And people can fake interviews and people are not telling the truth necessarily on resumes. I've had that experience myself with people I've hired and it's time-consuming to hire people. So I think for some hiring managers, or recruiters, it's a shortcut.
But is it sometimes shortcuts don't get you where you wanna go? So, this is an issue, I think because sometimes like with the Meers Briggs, for example, I know it's been used in a lot of hiring processes and I know the MBTI pretty well say you have a group and you got their MBTI scores and you go, this is a pretty high functioning group, right?
Or people are talented. Let me hire like that based on score. Okay. But. Are you getting the most variety of perspectives? Are you cloning again? If you get so many people that are so much similar to one another in by virtue of something about them, the M B T I score, whatever, then you're going eventually in the short run, maybe it's easier to function together, but in the medium and long run, and there's a lot of research to prove this you're gonna be in trouble.
You don't get effectiveness longer-term effectiveness by cloning on any basis.
Jeff Hunt:
So really what you're saying is that by using some of these assessment tools, as part of the recruiting process, we could have a counter effect on our diversity inclusion initiatives. We could end up further solidifying our lack of diversity, cuz we're always going for the same type of person.
Because they have proven to be an effective team member or they're contributing to the culture, but they're not helping us make better decisions or things like that. Is that correct?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Right. And then the other issue is maybe they were good for the as-is state. But if you look at creating the organization, the culture you want in the future, is that gonna get you where you wanna go?
A lot of times there's a default to trying to use Enneagram tests, just for example, And the Enneagram, as I said, cannot really be used for hiring, but you can make a lot of errors that way, but the tests are only about 65 to 70% accurate anyway.
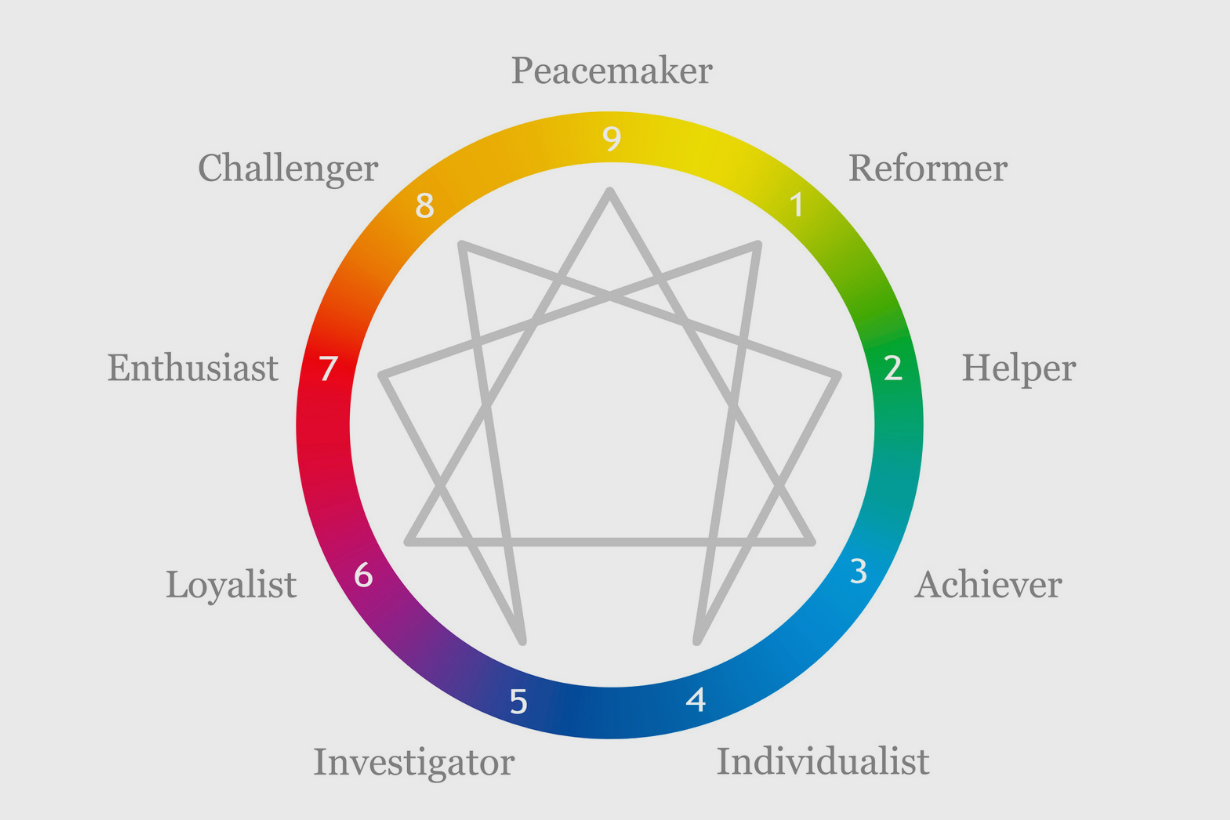
Topic 3. The Enneagram (10:22)
Jeff Hunt:
Sure, that makes sense. Share a little bit more about the Enneagram. You mentioned it's three or 4,000 years old. That's just ridiculously old. So, I assume it was sort of passed down orally traditionally.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Yeah. Originally, and then things were added to the system and etcetera. So that's exactly right.
Jeff Hunt:
So give us an overview of what it is for those people that are not familiar with it.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So, there are nine types each with a distinct pattern of thinking.
A pattern of emotional response pattern habitual, and a tendency to act in certain ways, no type is better than any other type. Although sometimes people wanna think so, it's not the truth. They're just different. The thing about the Enneagram that's really, I think, astounding, is it shows you a mirror of who you actually are.
And also it's a development system, so it's not about, okay, this is how you are. You can understand yourself better and you can accept yourself more, which is fantastic. But the second thing is, so it shows you how you can develop if you want to with specific, uh, development paths based on each type, which is super helpful.
So I'll go through the nine types. Okay. In terms of leadership style, but you know, I'll reference the type in general and then I'll give you, I hope a story that will be short.
Topic 4. Personality type 1 (11:41)
Jeff Hunt:
Okay, perfect. And before you jump in real quick, it sounds like what you're saying is actually it's very pragmatic. Because when you know your type, there are these very obvious sorts of areas that you can work on. On a regular basis to really move and live into your higher self. Is that correct?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So, the thing, you know, I'm gonna do it to leadership, but you could lead it to parent, teachings. It's about how to communicate more effectively. It's about how to deal with conflict, cuz there are Royal patterns by type. Well, how do we deal with conflict, and how do we respond to it? Are we helping ourselves?
What are some additional ways it's around more choicefulness? So let me start with, I'll start with, I'll go one through nine. Okay. So we'll start with type one. There. Books and people that will give them labels for each of the types. I tend not to do that because I don't like labeling anyway.
And I think Enneagram is about showing you who you are and helping you move beyond a label. So I won't do that, but in type one, they're really seeking perfection. Although they know they won't be perfect and they're not, it's constant wanting to be, and they're avoiding making mistakes. They really don't like that.
So they're trying to get everything right. So one leader. Their leadership style tends to be this they see a leader's job is to set clear objectives. And inspire others to achieve the highest quality, super high standards. Often leading by example, very clear and precise. They tend to be very pragmatic, but developmentally need to relax control, cuz they like to control everything.
That's how you get it as perfect as possible. And delegating is difficult because nobody can do it quite as well to the standard. So, one of my clients, who's a one was in a group of peers and this person said, I can delegate. I can delegate to this person who had a span of 45 employees who worked in that space.
And so that person said, well, I can delegate. Well, how many people PI says, well, two people. Well, why only too, because I only delegate to people who can do it better than me and somebody else in the group said, Hey, your job as a leader is to develop people as well. What it would be like if you could do it with people, delegate people who could do it, as well as you, that would be five people.
They said, well, you need to expand it. Who can do it 80% as well. And then you develop them. So that's type one.
Topic 5. Personality type 2 (14:05)
Jeff Hunt:
Okay, so let's hear about type two
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Well, this is a type, which is my type, that's very focused on how other people and helping them do something more effectively-being, finding out tuning into what their needs.
They're very intuitive. They tend to focus on others, much less on themselves. So they think the leader's job is to assess the strengths and weaknesses of team members. And they're really good at it and then motivate their team members towards the achievement of what the organization's wanting to accomplish.
Now, these are all different, but they're all really effective. But then you get into a narrow view, like effective in certain circumstances and maybe not so much in others, right? So the strengths tend to be being empathic and motivating other people and development areas, setting boundaries saying, no, no, you can't do this.
No, that wasn't okay. And setting boundaries so people hear them and delivering difficult information. Usually good at giving feedback, but when what's emotional and you care about the person or you think they're gonna have a strong negative reaction, very difficult. They're also sensitive to the environment.
I know several twos who are in leadership and they really tried to change the culture of the organization to be more people-oriented and positive and they couldn't do it. And so what did they end up doing? They got very frustrated. They kept trying and they left precipitously. And that's a big loss to the organization because they weren't able to influence the way they wanted to.
In the world of two, if it's painful and people are suffering, I can't bear to be in this.
Jeff Hunt:
It sounds like twos care deeply about others and they care deeply about improving the situation.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
But less self-care. So the leaving it's really got to the person and they weren't taking care of themselves.
Trying so hard to take care of others that they ended up leaving the organization. And possibly regretting it.
Jeff Hunt:
So the tendency of the two could be to sacrifice themselves for the gain of the organization or whatever they’re dealing with.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Exactly, but then you sacrifice and then you gave away so much. And don't take care of yourself.
Jeff Hunt:
The other thing that's helpful as you're explaining these is for people to listen to them in terms of which type they think they might be. So, if listeners can kind of have an open ear to that, and I would say that a key takeaway there too, at least for myself, was when I listened to my type.
In some ways it described me and it's like, oh yeah, that's me. But then it also made me cringe a little bit. So, if those are what you're experiencing, then that could be your type.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So now we're gonna get to your cringe. Although I know you've been working on yourself, so I hope that the more you work on yourself and that's true for me, I cringe less on my type and work more on the development.
Topic 6. Personality type 3 (17:01)
Jeff Hunt:
Yes. So type three, my type. Let's hear it.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
All right. So this is the type that's results, results, results. Ready in fire wanting results, wanting to perceive oneself as successful or competent. Do they define success by their own term? They do but avoiding failure, that's like at all costs.
So, what happens, their style of leadership is they like to set goals and create plans automatically and then deliver on them. So, they create an environment that achieves results and they think that happens when people understand the organization's goals and structure. So, their strength getting results and staying focused, staying really focused on the deliverables and the results, but the development can be very impatient when things are not moving fast enough and afraid to take risks that where they might fail.
And that's a really, even in one's personal life, my son who's a three. He never would swim because he didn't feel like he could be successful with his feet off the ground. So he's fabulous. Went any sport. Except not his feet off the ground that made him anxious, right? Now he's starting to take the risk and swim and it's okay.
And he's even enjoying the process. So, you know, though, they can be super-competent, but when they feel like they're risking failure or they can overwork themselves because they don't wanna fail, then they can get interpersonally abrupt. The way I say it is the person who could teach charm school needs to go to it.
We like that, that you wanna give a story about yourself, Jeff?
Jeff Hunt:
Yeah. Well, I appreciate that description and I'm reflecting on sometimes as a three. What happens for me is I am so goal oriented and focused that I will lose sight of the important connections that I need to be maintaining and keeping with my team.
It's very interesting too, because obviously I run a software company and our software is, you know, the name of my company is GoalSpan. So that's sort of right into the three dom, but I will also add ginger that it's pretty incredible when you look across this country because it's filled with threes and many business leaders and CEOs or executives, people in the C suit.
Are threes now, not always the case, but they get fueled and encouraged and motivated by societal norms and encouragement for this achievement orientation, which oftentimes for people that achievement orientation can be at the expense of a more fulfilling life. So that's a bigger picture discussion that we could probably take offline somewhere else, but.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Well, I'd also add countries. Many countries have a type culture and the US is a type three. Although different regions are not. And in corporate America, it tends to be a little bit three-ish, but doesn't mean all the leaders are threes. So sometimes, and it's for your audience. People might mistake themselves for threes when they're not because the culture of the organization has sort of required them to be very three-like.
Jeff Hunt:
One more thing on the three before we move on, I'm sort of thinking about how threes can be leaders, but this is goes back to your original point of being careful to value every single type on the Enneagram. Because if we can fill our leadership teams with a diversity of types, we're gonna end up making better decisions.
If I fill my leadership team with a group of threes. Then we're gonna be a little bit more narrow minded than we would be otherwise, even though we're achievement oriented, but it's also gonna probably have a negative effect on our overall culture. Wouldn't you agree with that?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Well, hypothetically, I think it varies whether they're filled with three, right.
But I think it depends on the company, but let's hypothetically say that the most corporations run by a lot of threes, right? What are you gonna get? You're gonna get results. You're gonna get measurable objectives, but what might you not get? Enough attention to people, enough attention to development, enough attention to risk taking, because right now, you know, we're in a, a place where 10 or 15 years ago, there wasn't such a need to take risks, right?
There was more stability. Now we're an unknown territory. There is a need to take risks. So, if the fear of failure is looming and that's your failure avoidant type that could impact your willingness to take risks.
Topic 7. Personality type 4 (21:35)
Jeff Hunt:
Yes, that makes sense.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So, but anyway, type four fours like to think of themselves as different, unique, and special, and they tend to be the most internally oriented of all the nine types.
So, they're looking at meaning and purpose and vision and real and deep inspiration. That's really cool because they sit right next numerically to threes that are focused on the external drive for results and plans. Here you have a type let's find purpose and meaning in the work we do, which is really, really important, so we can do excellent work.
So, the strengths are creating a deep vision and connecting with others emotionally. I mean, they will hang in there, whereas the threes can be impatient and other types can be more impatient, not the four so much. But what are the development areas? Well, not taking things personally that happen.
And being able to regulate their feelings internally, cuz they're very feeling responsive. So I had a client who I was tasked to give feedback to this person, as well as several others and to collect feedback and use the underground typing to help them understand how they were processing, what the feedback might be.
Now, the interesting thing, this person was a four. Was so anxious about getting the feedback from me. And the question I asked was why, because in a prior job, they had gotten some feedback and it had been very negative. Now the feedback I had on this person was hugely positive. That person didn't know it yet, but the pain of having gotten negative feedback 20 years earlier, 15 years earlier, was so deeply in this person that the fear and the pain, I mean, it was awful.
So, then I knew I had all this positive to say, but we got through that. And when I gave this person positive feedback, seriously, they slept across their desk. The person was almost twice as tall as me. To hug me. The relief was huge.
Jeff Hunt:
I love that story. And I'll just say that one of the things that seems important if you truly understand the nine types, if I'm gonna go provide feedback to a four, and I understand what their tendency would be in terms of how they receive that feedback, I might tweak my approach a little bit.
So that we can end up with a better and more valuable conversation. And then the second thing I would say is, it sounds like what you're saying is we should really lean on fours when it comes to things like vision casting within our strategic planning process, we should make sure that they have a big seat at the table to help us guide the organizational direction.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Okay. So I have a different take, I say yes and. If you have a very skilled for the job and experienced for and they're at the table, which is great. Let them influence you to get more visionary yourself, let them really find that inspiration in you. So like we don't rely on the threes to kind of set objectives and results.
Right? We can find that in us, we don't rely on the twos to try to motivate, to figure out what people need and want. They can help us bring that out in ourselves. That's maybe my message.
Topic 8. Personality type 5 (24:40)
Jeff Hunt:
Great. I love that.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So fives like things to be objective and logical and systematic.
They're very mentally cerebrally oriented and they disconnect from their feelings in real-time. Go off and have them later though. So in some sense, the fives are almost the purest feeling. They just don't experience it in real-time. So they believe that a leader's job is to develop an effective organization through research, deliberation, and planning.
So it's ready, ready, aim, ready, ready, aim, fire. And they want all systems to fit together so that people are working on a common mission. So their strengths are being objective and being logical in the way they approach things. What are the development areas? Well, it's approachability because if you disconnect from feelings in real-time and you kind of keep a little distance, people don't know how to read you and emotional connectivity, they do connect when people they want to emotionally can be at work are gonna be at home, but they’re selective.
They're very selective. So they need to not feel like we're intruding on them. You know, they need 50% more space if we're in physical proximity to them. And the normal space between people in the culture you're in varies by culture is, might be 12 or 18 inches. Add six more.
Interesting. It's 18 add nine, you know, something like that. They just like, they don't wanna feel like somebody's coming too close. So most of the five leaders that I coach, it's amazing, they get some very similar feedback, which is people feel like they, they may respect them, but they don't feel like they know them.
What I tell the five leaders is it's not that they really want to know you. They think they do. They want you to feel that you know them, they're looking for connectivity. So, I usually coach them to don't feel obligated to share stuff that you don't want to, but spend time with people, ask them how they're doing and listen.
Topic 9. Personality type 6 (26:39)
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
So let's go to six. So sixes are the most complex of the nine types, and this is a type that believes that the world is not, it's not certainty and predictability in the world. So they're trying to figure out how to make it a more certain world and they know it's not a certain world.
So, they have an ex relationship to risk, risk avoidant risk. Wanting to go into risk to prove that they're not risk averse afraid, you know, it's kind of fun. Some of them are just very dutiful to the team and to the organization, so that avoids their risks and create little tribes or families around them.
So they believe that a leader's job is to solve organizational problems by developing a creative problem solving environment. So, every person feels that they are part of the solution strengths, problem solving, perceiving alternative pathways. Development is too little or too much risk taking and skepticism continuously asking what ifs, what ifs.
Which can selectively be good, but too much they can get the perception of that they're keeping the group or the team oration from moving forward. Cuz they keep, what about this? What about that? Well, actually sixes would prefer other people would ask that. So they didn't feel like they had to keep asking.
Jeff Hunt:
Sixes may be the ones in the leadership team that are willing to ask those questions that other people aren't.
So it sounds like it's a matter of balance. We want to hear from the sixes in terms of their questions to help us mitigate risk. But we want to do that with the correct lens and the right balance.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Now I have one six client who was the kind of six that would go against the fear with action. And it was a little hard to see that there was this risk thing.
The person's team member said we would follow this leader anywhere. And I said, over a cliff, Yes if our leader said it was safe over the cliff and I went, okay, this is a version of six also. Wow. Cause they can be quite charming. They may not show that they're playing risk.
Topic 10. Personality type 7 (28:12)
Jeff Hunt: What is the seven, and their tendencies?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
All right. So sevens are the most optimistic of all of the Enneagram types. And although, we might think of optimism as a good thing, which it is, but we're talking about like super optimistic, like everything's good and everything's possible. And the fewest limitations, nobody has the right to restrict me.
We can do anything we want to. Often they think with the right people and the right team we can do everything, which isn't a course in a sense is that really grounded in reality, but it is very action-oriented, but they love idea generation. That's what stimulates them. And I wanna think because I know some of the people listening or go, well, I like ideas and I'm creative and all it's not about creativity.
It's about idea generation. Some sevens are more creative than others. It's just like really getting enamored of ideas and sometimes liking the ideas as much or more than the execution. So they believe that a leader's job is to get people excited and to create innovative ideas and ventures so that the organization can take advantage of new and important business opportunities.
So some of the strengths are being very innovative and listening to others in their vision. They love that. But the development areas, being able to stay focused, and the attention span is really challenging. You say something and they're on to something else. They have minds that kind of move from idea to idea, concept to concept so quickly.
It's like a computer mind where there are no file folders. Everything's a document and they have challenges adhering to limits. They hate the word no, it's not in their vocabulary. I see now I've had a number of seven clients, but one who's been a long-term client. This leader of seven wanted everybody on the team, the senior leadership team to put their own ideas forward and couldn't understand why they weren't.
Why? Because this person had so many ideas viewing coming that there wasn't much space and time for anybody else to add. Other people were having challenges, understanding the ideas cuz they were happening so quickly to even process there's also a challenge. What are we supposed to execute on? Which of the ideas does this leader like?
Are these just ideas? And if we start adding our own, even if we have the space to instead of 20 thing ideas, now we're at 30 and more and we're overwhelmed. So it can be a little challenging to people who work for leaders who are sevens, who might really enjoy working for them.
But it's like, what do we focus on here?
Jeff Hunt:
So it sounds like the seven can be motivating and inspiring and they're filled with energy and they're bringing this life to the team and they have all these ideas. And they're gonna bring this level of energy that might not exist otherwise. But it also sounds like the challenge is reigning that in a little bit so that we retain some focus and we retain some direction and we retain enough margin in the group for others to contribute. Is that correct?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Right. The leader thought I'm asking them to contribute. Didn't understand why they didn't. There wasn't any space between thoughts. Sometimes the sevens, I had another seven clients I said to this person, do you ever breathe? because the words were, and ideas were coming so fast. And that, you know, it's like, you're not breathing, there's no space for other people to contribute to the system.
Jeff Hunt:
I'll add a footnote to the seven before we move on to the eight. So you mentioned your son. Well, my younger son is also a seven, so he happens to be a musician. And we, for those of you that are interested between episodes 25 and 26. we recorded a bonus episode where I had the opportunity to interview him.
He's very familiar with the Enneagram. He knows he is a seven and he wrote a song called still that episode he goes into the value of being present. Both in the workplace. And he brought his experiences from being a camp counselor sort of into the episode.
And we unpacked those from a leadership lens, but it seems like when the seven can have the ability to really arrive and be present. Then there's this opportunity to show up in a new way. That's really gonna enhance things.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
My reaction to your story. I imagine you are very proud of him for that because not only is creative and all but being still is one of the most challenging things for a seven.
They're always in motion. Their minds are in motion. They use their arms, a lot to explain and they often pace and they need to be moving and really moving. So, to be still is to be present, but for any of us, but to be dealing with our emotions, cuz there's a way that sevens do move away from their emotions except joy.
They love that. And so the name of the song, the piece is still, I mean, that's just so amazing.
Topic 11. Personality type 8 (33:52)
Jeff Hunt:
Yeah. I'm very proud of him, so okay. Number 8!
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Type 8 okay. So eight are the big bold, you know, superheroes or so they think of themselves. They can take the city. They're supposed to protect the weak, the victimized, although they don't like weakness in others at all.
Cuz they need to be strong and bold. But if people are being abused or being treated poorly, they are the first to show up and be the big defenders. And if you understand it, it's like only the powerful can defend are big enough to defend the weak, right? It kind of works. And in leadership, they believe that their job is to move the organization forward by leading decisively.
Getting capable and reliable people in the right jobs. Then they can trust your work and empowering competent people to take action. They don't empower people that they don't perceive as competent, but if they don't perceive you as competent and they have anything choice about it, you won't be working for them very long.
So their strengths can be taking charge and being assertive. But the development areas, of course, each type has both sides being receptive to others' opinions. The eight are a type that kind of trusts their gut reaction. If they have a reaction to something or about action or about an individual, they kind of believe that's the truth.
And they're often not as receptive to others. So it's about sometimes you need to be receptive. You can't always trust your gut about people. They like big action. They don't like medium action. They don't like small actions. It's gotta be big. So sometimes big action isn't what's called for, but their guts say take this big action and they can overextend themselves tremendously.
They go into like overhaul, overwork, overdue. I don't wanna concern about people too much, but I need to say this. Sometimes they don't pay attention to how overworked they are or their physical well-being, and they can land up in the hospital out of sheer exhaustion. Or there could be something wrong, but they power through some ailment and then it can be serious.
So it's about really paying attention, not to just moving powering forward, but to whether you're leading a team powering forward or you're pushing yourself to power forward and power on it's to also allow yourself to power down and be, and pay attention to what's really going on and to be more receptive.
Jeff Hunt:
So for eights, it's paying attention internally to what's going on and whether they actually are overworking and whether they are listening in.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Or overeating or undereating or over-exercising or under-exercising, or, you know, over, under, they tend to go either over or under.
Jeff Hunt:
Sure. And then it's a matter of also paying attention externally. So, on your team, for instance, make sure to pay attention. Are you allowing other viewpoints? Are you really allowing enough space for people to provide a viewpoint and inform the decision? The other thing I'm getting the sense about the eight Ginger, it sounds like the way you've described them, they're showing up with a big presence. Is that often the case as they sort of.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Yes, some are more introverted. Like anybody and some are quieter, which doesn't mean you're introverted, but their presence is felt whether they're talking or they're not talking.
And they know how to power up energetically somatically.
Topic 12. Personality type 9 (37:11)
Jeff Hunt:
All right. Type nine.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
The nine, the kind of viewpoint is I go along to get along. I want harmony. I want everybody to feel part of this. They tend to really value consensus, with everybody having a voice. Being respectful, and not being rude is super important to them. So they believe their job is to help everyone achieve the collective mission through a clearly structured, harmonious work environment.
So sometimes it's like people say about minds, they don't like conflict. That's partly true. They don't create disharmony, but on the other hand, they're super good at mediating conflict between others. They listen to you, they nod their heads. They understand multiple perspectives.
I've seen nines, mediate conflict between two others, whether the two other people didn't even need to get together, they felt so listened to and understood. So there are strengths of the nine leaders, creating consensus and listening to multiple viewpoints and they really do value multiple viewpoints. But then on the other hand, developmentally taking a firm stand.
Sometimes it can be very hard for nines and leaders do need to take stands. But the question is what, when and how right. But for nines, it can be hard to take a stand because they don't wanna create tension and conflict. And sometimes they're not quite sure because they see so many perspectives.
What their stand is. And sometimes they wanna hear everybody else cuz they like what amongst all these viewpoints what be common ground. But they do leaders do need to take a stand. Sometimes it's important for nine leaders to develop that. And then they need to also learn how to face conflict directly and not get throttled.
Cuz many nines feel it in their bodies when there's conflict directed at them or they're angry. They often will not let themselves be aware that they're angry, but they are, but they feel it in their bodies. Right. And then they cause themselves that causes them to not sleep so well and to feel the tension and, you know, it's uncomfortable. And so it's about learning how to do that.
Topic 13. Lighting round questions (39:08)
Jeff Hunt:
Seems like the work of the nine is really to be able to maybe process that emotion, but then let go eventually. And actually, I guess, look at those situations, proportionally for what they really are not overplayed or overblown. Okay. Great. So we've now covered all the nine types and, that was a great overview.
So thank you so much for that. I'd love to shift before we wrap up today's episode and just ask you a few quick lightning-round questions and shift away from the Enneagram for a second. So are you ready for that?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Oh, of course, I am.
Jeff Hunt:
All right. So the first one is what are you the most grateful for?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
My son. He's 31, a great teacher.
Jeff Hunt:
Ginger, if you look back on your career, what was the most difficult leadership lesson that you've learned?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
What I've learned is I can only do the best I can do at the moment. And there will be times when people don't like it or misread it or whatever, and I have to be okay with that. That's part of being what a leader is.
Jeff Hunt:
Who is one person you would interview if you could living or not?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Barack Obama. Or maybe Zelensky yeah. I'd wanna interview him. Cause I don't know how he stepped up into this the way he did. I mean, that's about rising to the occasion, really rising to the occasion.
Jeff Hunt:
He's quite a leader, isn't he? Absolutely. Okay. Let's quickly summarize today's episode. It sounds like what you're saying is this Enneagram thing is a very, very old tool that has evolved over the ages it's become more modernized. And now its adaptability to business provides tremendous value.
And each of these types, if I understand you correctly is not about putting people into a box, but it's more about helping them get out of the box. Is that a good way to say it?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Perfect. That's exactly right.
Jeff Hunt:
And what else can you share to help summarize our conversation today? Anything else you want our listeners to know from today's episode?
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
Yeah, I think it's about approaching the Enneagram system, yourself, and others with curiosity and not judgment.
Jeff Hunt:
That's great. That's quite a leadership lesson for all of us. That lens of curiosity. Well, ginger, thank you so much for coming on the episode today. I really appreciate all the wisdom you shared with our listeners.
Ginger Lapid-Bogda:
I enjoyed it.
Outro(41:39)
Closing music jingle/sound effects
Jeff Hunt:
Thanks for listening to the show this week. We release new episodes every other Tuesday. Let me know what you thought of this episode by emailing humancapitalgoalspan.com. Human capital is produced by GoalSpan. Subscribe, wherever you get your podcasts. And please share this podcast with your colleagues, team, or friends. Thanks for being human kind.

 Apple Podcasts
Apple Podcasts
 YouTube Music
YouTube Music
 Spotify
Spotify
 Pandora
Pandora
 Breaker
Breaker
 Castbox
Castbox
 Castro
Castro
 Himalaya
Himalaya
 iHeartRadio
iHeartRadio
 Luminary
Luminary
 Overcast
Overcast
 PlayerFM
PlayerFM
 Pocket Casts
Pocket Casts
 Podbean
Podbean
 Podcast Addict
Podcast Addict
 Podcast Republic
Podcast Republic
 RadioPublic
RadioPublic
 RSS Radio
RSS Radio
 SoundCloud
SoundCloud
 TuneIn
TuneIn